Views: 1
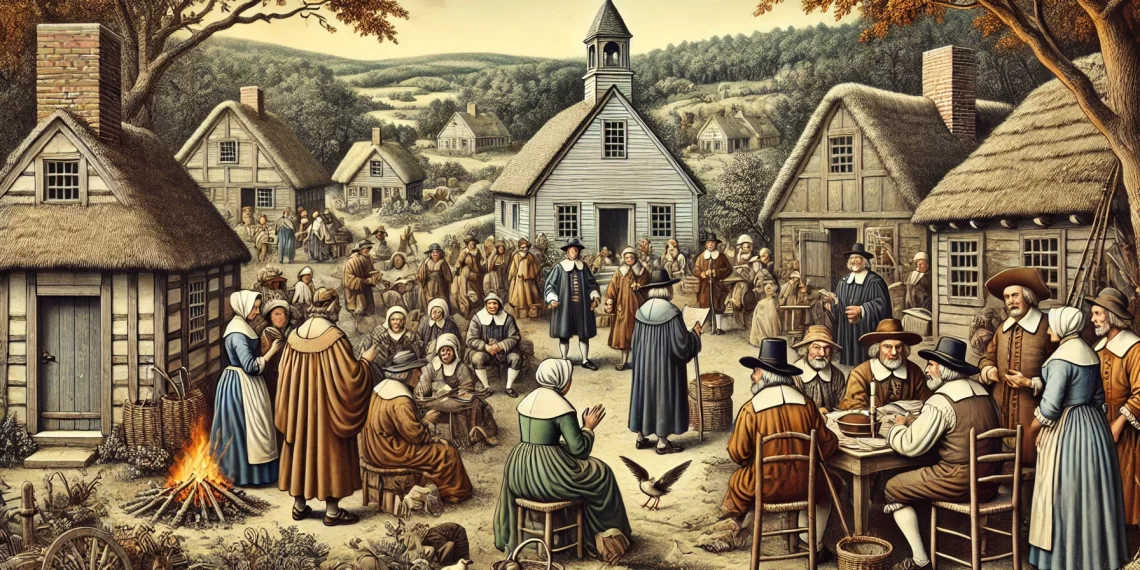
Lesson Title: The Puritan Movement: Study of the Puritans and Their Influence on American Christianity
Level of Education
Doctoral Degree in Biblical Studies
Purpose
To explore the origins, beliefs, and lasting impact of the Puritan movement on American Christianity and society.
Objectives
To understand the theological principles of the Puritans, their migration to America, and their influence on American religious and cultural life.
Key Concepts, Terms, and Keywords
- Puritans: A group of English Reformed Protestants who sought to “purify” the Church of England from its Catholic practices.
- Covenant Theology: The Puritan belief in a covenantal relationship with God, emphasizing communal and individual responsibilities.
- The Great Migration: The movement of Puritans from England to America in the early 17th century.
- Religious Freedom: The Puritan quest for a place to practice their faith freely, influencing American concepts of religious liberty.
- Work Ethic: The Puritan belief in hard work, discipline, and frugality as expressions of faith.
Lesson Content
- Historical Context:
- Origins and Beliefs: Overview of the Puritans’ theological roots and their desire to reform the Church of England.
- Bible Verses: 2 Corinthians 6:17; Hebrews 12:14
- 2 Corinthians 6:17 calls for separation from impurity.
- Hebrews 12:14 emphasizes the pursuit of holiness.
- The Great Migration:
- Reasons for Migration: Religious persecution and the desire for a “city upon a hill.”
- Establishment in America: Founding of colonies with a focus on religious and moral order.
- Bible Verses: Psalm 107:1-3; Matthew 5:14-16
- Psalm 107:1-3 speaks of gathering from exile.
- Matthew 5:14-16 refers to being a light to the world.
- Bible Verses: Psalm 107:1-3; Matthew 5:14-16
- Theological Principles:
- Covenant Theology: The belief in a collective covenant with God.
- Bible Verses: Exodus 19:5-6; Jeremiah 31:31-33
- Exodus 19:5-6 describes Israel as God’s treasured possession.
- Jeremiah 31:31-33 speaks of a new covenant with God’s people.
- Bible Verses: Exodus 19:5-6; Jeremiah 31:31-33
- Predestination and Election: The belief in God’s sovereign choice in salvation.
- Bible Verses: Romans 8:29-30; Ephesians 1:4-5
- Romans 8:29-30 outlines predestination.
- Ephesians 1:4-5 speaks of being chosen by God.
- Bible Verses: Romans 8:29-30; Ephesians 1:4-5
- Covenant Theology: The belief in a collective covenant with God.
- Influence on American Society:
- Education and Literacy: Establishment of schools and colleges, including Harvard.
- Work Ethic and Morality: Influence on American values of hard work, discipline, and community responsibility.
- Bible Verses: Proverbs 6:6-8; Colossians 3:23-24
- Proverbs 6:6-8 emphasizes diligence.
- Colossians 3:23-24 encourages working heartily as for the Lord.
- Bible Verses: Proverbs 6:6-8; Colossians 3:23-24
- Religious Freedom and Legacy:
- Impact on Religious Liberty: Contribution to the development of religious freedom in America.
- Enduring Legacy: Lasting influence on American religious and cultural identity.
- Bible Verses: Galatians 5:1; John 8:32
- Galatians 5:1 speaks of freedom in Christ.
- John 8:32 emphasizes the truth setting believers free.
- Bible Verses: Galatians 5:1; John 8:32
- King Jesus’ Model/Example:
- Discipleship and Community: Jesus’ teachings on community living and moral integrity.
- Bible Verses: Matthew 18:20; John 13:34-35
- Matthew 18:20 emphasizes gathering in Jesus’ name.
- John 13:34-35 commands loving one another as Jesus loved.
- Bible Verses: Matthew 18:20; John 13:34-35
- Discipleship and Community: Jesus’ teachings on community living and moral integrity.
Exam Questions with Explained Answers
- Question: What were the main theological principles of the Puritans?
- Answer: The Puritans emphasized covenant theology, predestination, and a commitment to moral purity and community responsibility, reflecting their desire to live in accordance with biblical principles (Exodus 19:5-6; Romans 8:29-30).
- Question: How did the Great Migration shape the development of American colonies?
- Answer: The Great Migration brought Puritans to America, where they established colonies based on religious and moral order, aiming to create a “city upon a hill” as an example of godly living (Psalm 107:1-3; Matthew 5:14-16).
- Question: Explain the concept of covenant theology and its significance to the Puritans.
- Answer: Covenant theology is the belief in a collective covenant with God, where communities and individuals are bound by mutual obligations to uphold God’s laws, fostering a sense of communal responsibility (Jeremiah 31:31-33).
- Question: What role did education play in Puritan society?
- Answer: Education was highly valued by the Puritans, who established schools and colleges, such as Harvard, to ensure religious and moral instruction, thereby promoting literacy and scholarly pursuits (Proverbs 6:6-8).
- Question: How did Puritan beliefs influence American work ethic and morality?
- Answer: The Puritan emphasis on hard work, discipline, and community responsibility shaped American values, promoting a strong work ethic and moral integrity as expressions of faith (Colossians 3:23-24).
- Question: Discuss the Puritan contribution to the concept of religious freedom in America.
- Answer: The Puritan quest for a place to practice their faith freely contributed to the development of religious liberty in America, influencing the nation’s commitment to protecting individual religious rights (Galatians 5:1).
- Question: What was the significance of the Puritan belief in predestination?
- Answer: The belief in predestination emphasized God’s sovereign choice in salvation, shaping Puritan attitudes towards faith, humility, and the assurance of God’s plan for their lives (Ephesians 1:4-5).
- Question: How did Puritan practices reflect their commitment to community and discipleship?
- Answer: Puritan practices, such as communal worship and moral accountability, reflected their commitment to living out Jesus’ teachings on community and discipleship (John 13:34-35).
- Question: In what ways did the Puritan movement leave a lasting legacy on American Christianity?
- Answer: The Puritan movement left a lasting legacy on American Christianity through its emphasis on biblical authority, moral living, and the establishment of religious and educational institutions that continue to influence American religious and cultural identity (John 8:32).
- Question: How did the Puritans’ pursuit of a “city upon a hill” shape their vision for society?
- Answer: The Puritans’ pursuit of a “city upon a hill” inspired them to create a society based on biblical principles, aiming to serve as a model of godly living and moral integrity for the world to see (Matthew 5:14-16).
Practical Applications
- Community Building: Foster strong, supportive church communities that reflect Puritan values of mutual responsibility and moral accountability.
- Educational Commitment: Emphasize the importance of religious education and literacy in personal and communal faith development.
- Work Ethic: Encourage diligence and discipline in all areas of life as expressions of faith and devotion to God.
Research Citations
- Bremer, Francis J. “The Puritan Experiment: New England Society from Bradford to Edwards.” University Press of New England, 1995. eBook.
- Morgan, Edmund S. “The Puritan Dilemma: The Story of John Winthrop.” Pearson, 2006. eBook.
- Winship, Michael P. “Hot Protestants: A History of Puritanism in England and America.” Yale University Press, 2018. eBook.
- Hall, David D. “The Puritans: A Transatlantic History.” Princeton University Press, 2019. eBook.
- Noll, Mark A. “America’s God: From Jonathan Edwards to Abraham Lincoln.” Oxford University Press, 2002. eBook.
This lesson provides a thorough exploration of the Puritan movement, highlighting its theological principles, historical context, and enduring influence on American Christianity and society.